目标
本文验证以下几点:
1. 创建派生类对象时,自动调用基类构造函数
2. 在C++中,有函数覆盖时,可以通过“派生类对象.基类::函数(参数)”的形式调用被覆盖的基类函数
3. 在C++中,允许以派生类对象为初始值创建基类对象,反之不行
4. 在C++中,允许把派生类对象赋值给基类对象,反之不行
5. 在C++中,可以把派生类对象的地址赋值给基类指针变量,反之不行
6. 在C++中,当基类指针变量指向派生类对象时,通过该指针调用非virtual函数,则只能调用基类的函数;通过该指针调用virtual函数,调用的是派生类的函数
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Animal //动物类,抽象类
{
protected:
int height; //身高
int weight; //体重
public:
Animal()
{
cout << "一个动物诞生了..." << endl;
}
void Move()
{
cout << "我的位置发生了移动..." << endl;
}
virtual string getClass() = 0;
};
class Monkey : public Animal //猴子类
{
protected:
int height; //身高
int weight; //体重
public:
Monkey()
{
height = 130;
weight = 40;
cout << "我是一只猴子" << endl;
}
void Move()
{
cout << "我跳到了树上" << endl;
}
string getClass()
{
return "Monkey";
}
};
class BlueMonkey : public Monkey //蓝色猴子类
{
protected:
int height; //身高
int weight; //体重
public:
BlueMonkey()
{
height = 130;
weight = 40;
cout << "我是一只蓝色的猴子" << endl;
}
void Move()
{
cout << "我跳到了树上" << endl;
}
string getClass()
{
return "BlueMonkey";
}
};
int main()
{
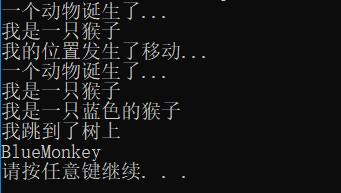
Monkey m; //验证第1点
m.Animal::Move(); //验证第2点
BlueMonkey bm;
Monkey m1 = bm; //验证第3点
m = bm; //验证第4点
Monkey *p;
p = &bm; //验证第5点
p->Move(); //验证第6点
cout << p->getClass() << endl; //验证第6点
system("pause");
return 0;
}